Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MariaDB order by clause to sort the result of a query.
Introduction to MariaDB order by clause
The select statement returns a result set whose rows are not in any specific order. To sort the rows of a result set by values in one or more columns, you use the order by clause.
The following shows the syntax of the select statement with an order by clause:
select
select_list
from
table_name
order by
sort_expression1 [asc | desc],
sort_expression2 [asc | desc],
...;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The order by clause appears at the end of a select statement.
In this syntax:
- First, specify one or more sort expression
sort_expression1,sort_expression2, … which can be columns or expressions by which you want to order. - Then, use
ascordescto sort the rows in the result set in ascending order (asc) or descending order (desc).
The order by clause uses asc by default.
MariaDB evaluates clauses of the select statement in the following orders: from, select and order by:

MariaDB order by clause examples
We’ll use the countries table from the sample database for the demonstration.

A) Using MariaDB order by clause to sort rows by one column example
The following select statement returns the names and areas of countries:
select
name,
area
from
countries
order by name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)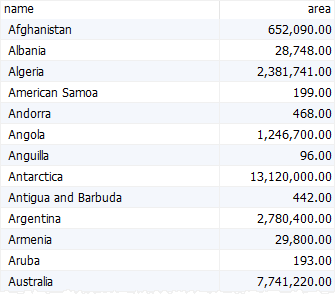
As you can see, the order of rows in the result set is not specified.
The following select statement uses the order by clause to sort countries by name:
select
name,
area
from
countries
order by
name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)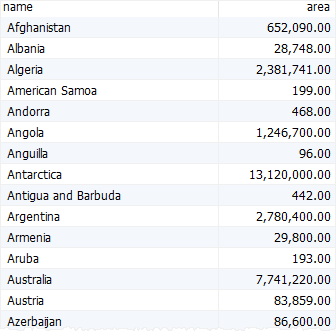
The order by clause sorted the countries by name in ascending order because it uses asc by default.
To sort the countries by name in descending order, you use the desc option:
select
name,
area
from
countries
order by
name desc;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)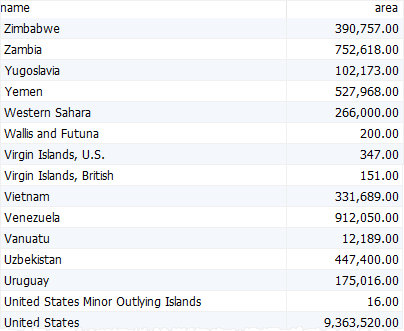
B) Using MariaDB order by clause to sort a result set by two columns example
The following statement uses the order by clause to sort countries by name and region_id:
select
name,
region_id
from
countries
order by
region_id,
name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)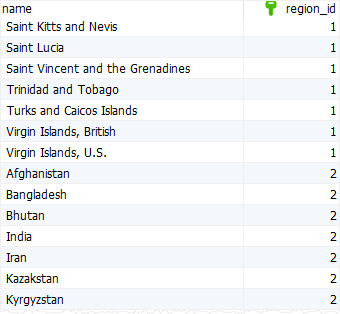
In this statement, the order by sorts the rows in the following sequence:
- First, sort the
countriesby values inregion_idcolumn from low to high. - Then, sort the sorted countries by values in the
namecolumn alphabetically.
MariaDB order by clause with null values
The null is a special value in MariaDB. The null indicates that a value is missing or not applicable.
MariaDB treats null as the lowest value so when you sort by a column that has null values, null values appear first in the result set.
The following statement uses the order by clause to sort countries by national days:
select
name,
national_day
from
countries
order by
national_day;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)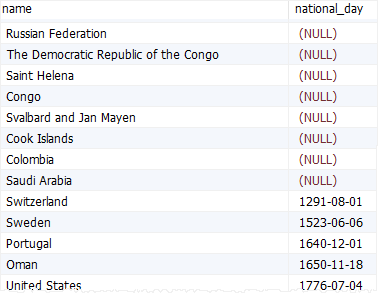
If you use the desc in this case, the null values will appear last in the result set:
select
name,
national_day
from
countries
order by
national_day desc;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)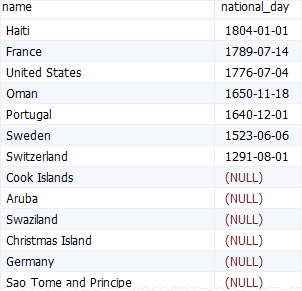
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MariaDB order by clause to sort a result set by values in one or more columns in ascending or descending order.